Science
Astronomers Uncover Rare Five-Point Einstein Cross in HerS-3
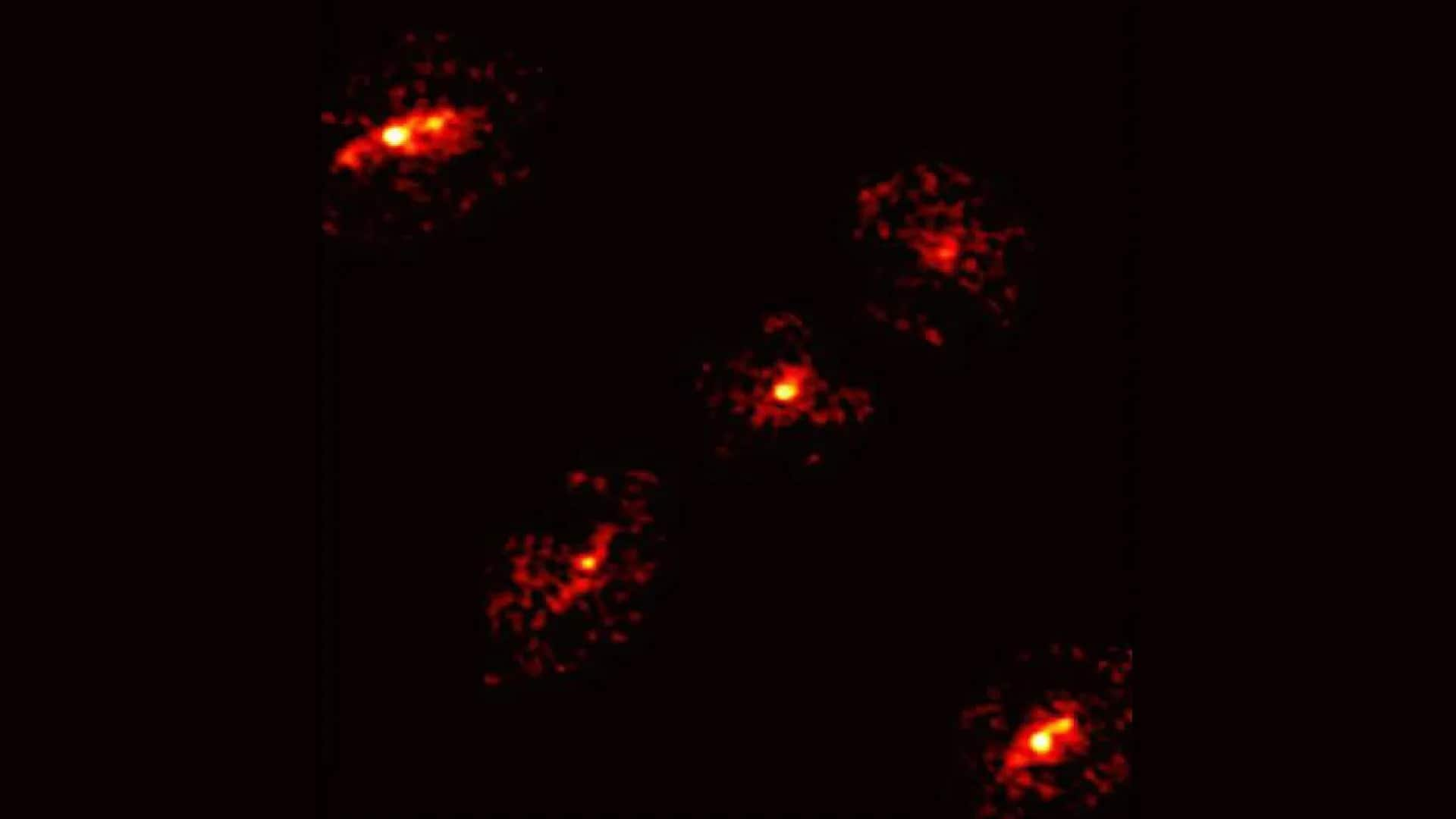
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery in the galaxy HerS-3, identifying a rare five-point Einstein cross, a phenomenon that typically features only four points of light. This anomaly, first detected by France’s Northern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA), has been validated through data collected from Chile’s Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and computer simulations.
An Einstein cross occurs when a massive object in the foreground bends the light from a more distant galaxy, resulting in multiple images of that background galaxy. The presence of a fifth point of light at the center of HerS-3 has prompted scientists to re-evaluate their instrument’s accuracy and the nature of the cosmic phenomenon. This discovery, detailed in a recent publication in The Astrophysical Journal, provides an important opportunity to explore the distribution of dark matter in galaxies.
Dark matter, an invisible substance that exerts a significant gravitational influence, plays a crucial role in cosmic structure formation. It can bend the paths of photons, creating light distortions that reveal insights into its distribution. The unexpected fifth point in HerS-3 is hypothesized to indicate a substantial region of dark matter, which could enhance our understanding of its role in the universe.
The research team employed computer models to investigate the phenomenon, ruling out the possibility of closer objects interfering with the light from HerS-3. They successfully modeled a dark matter halo in front of the galaxy, which aligned perfectly with the unusual light pattern observed. As dark matter does not interact with light, it remains invisible, but its gravitational effects are detectable through the motion of visible matter and light.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond mere observation. The additional light point in HerS-3 is believed to be a dark matter halo, capable of bending the light from background galaxies without being seen itself. This finding underscores the significance of dark matter in shaping the structure of the cosmos, providing scientists with a unique chance to study its influence on cosmic formations.
Astronomers continue to analyze data from HerS-3, seeking to deepen their understanding of dark matter’s distribution and behavior. The five-point Einstein cross stands as a testament to the evolving field of astrophysics and the insights that can emerge from unexpected anomalies in the universe.
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoSBI Announces QIP Floor Price at ₹811.05 Per Share
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoCept Unveils ₹3.1 Crore Urban Mobility Plan for Sustainable Growth
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoNew Blood Group Discovered in South Indian Woman at Rotary Centre
-

 World5 months ago
World5 months agoTorrential Rains Cause Flash Flooding in New York and New Jersey
-

 Top Stories5 months ago
Top Stories5 months agoKonkani Cultural Organisation to Host Pearl Jubilee in Abu Dhabi
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoBroad Advocates for Bowling Change Ahead of Final Test Against India
-

 Science5 months ago
Science5 months agoNothing Headphone 1 Review: A Bold Contender in Audio Design
-

 Top Stories5 months ago
Top Stories5 months agoAir India Crash Investigation Highlights Boeing Fuel Switch Concerns
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoIndian Stock Market Rebounds: Sensex and Nifty Rise After Four-Day Decline
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoCristian Totti Retires at 19: Pressure of Fame Takes Toll
-

 Politics5 months ago
Politics5 months agoAbandoned Doberman Finds New Home After Journey to Prague
-

 Top Stories5 months ago
Top Stories5 months agoPatna Bank Manager Abhishek Varun Found Dead in Well









